HUATUI
-
Welcome to our stand A110 CIAAF
-
Welcome to our stand W1.94 2025 CICEE
-
Welcome to our stand E1-A34 Yiwu Auto & Motorcycle Parts Expo 2025
-
Warmly celebrate the thoroughly successful ending of the 2025 China Hangzhou International Automobile and Motorcycle Parts Industry Expo
-
Welcome to our stand H7-R22 CAPAFAIR Hangzhou 2025
-
Welcome To Our Stand 9 E3617, BICES
-
Welcome to MIMS Automobility Moscow!
-
New Arrival ! Temperature Sensor For Caterpillar
-
New Arrival ! Fuel Water Level Sensor For Caterpillar
-
New Arrival ! Engine speed sensor For Caterpillar
-
New Arrival ! Crankshaft Postion Sensor For Detroit Diesel
-
New Arrival ! Solenoid Valve For Caterpillar
-
New Arrival ! Fuel Transfer Pump For Komatsu
-
New Arrival ! Solenoid Valve For Caterpillar
-
New Arrival ! Postion Sensor For Caterpillar
-
New Arrival ! Temperature Sensor For Caterpillar
-
New Arrival ! Solenoid Valve For Caterpillar--KEYOPO
-
New Arrival ! Speed Sensor For Caterpillar--KEYOPO
-
New Arrival ! Pressure Sensor For Caterpillar--KEYOPO
-
New Arrival ! Pressure Sensor For Caterpillar--KEYOPO
-
New Arrival ! Postion Sensor For Komatsu--KEYOPO
-
New Arrival ! Postion Sensor For Komatsu--KEYOPO
-
New Arrival ! Postion Sensor For Caterpillar--KEYOPO
-
Welcome to the Automechanika!
-
New Arrival ! Temperature Sensor For Caterpillar--KEYOPO
-
Welcome To Our Stand , Automechanika Shanghai
-
Happy New Year!
-
Do you want to know more about our product? Come and contact us!!
-
New Arrival ! Solenoid Valve For Caterpillar--KEYOPO
-
New Arrival ! Solenoid Valve For Caterpillar--KEYOPO
-
New Arrival ! Solenoid Valve For Komatsu--KEYOPO
-
New Arrival ! Solenoid Valve For BWM--KEYOPO
-
New Arrival ! Sensor For Komatsu--ROHOPE
-
Happy New Year!
-
New Arrival ! Solenoid Valve For Komatsu--KEYOPO
-
KEYOPO/RPHOPE Wish you a Merry Christmas!
-
Engine Starter Repair: How To Replace The Starter Solenoid
-
Common Bad Speed Sensor Symptoms
-
New Arrival ! Solenoid Valve For Caterpillar--KEYOPO
-
Advantages Of Solenoid Valves——KEYOPO
What is a Multimeter?
A
digital multimeter or DMM is a useful instrument for measuring voltage, current
and resistance, and some meters have a facility for testing transistors and
capacitors. You can also use it for checking continuity of wires and fuses. If
you like to DIY, do car maintenance or troubleshoot electronic or electrical
equipment, a multimeter is a handy accessory to have in your home toolkit.
1.Power
off the circuity/wiring under test if there is a danger of shorting out closely
spaced adjacent wires, terminals or other points which have differing voltages.
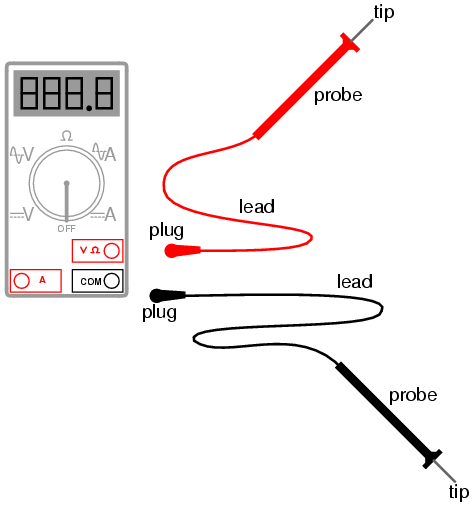
2.Plug
the black ground probe lead into the COM socket on the meter (see photo below).
3.Plug
the red positive probe lead into the socket marked V (usually also marked with
the Greek letter "omega" Ω and possibly a diode symbol).
4.If
the meter has has a
manual range setting dial, turn this to select AC or DC volts and pick a range
to give the required accuracy. So for instance measuring 12 volts on the 20
volt range will give more decimal places than on the 200 volt range.If the
meter is autoranging,
turn the dial to the 'V' setting with the symbol for AC or DC.
5.A multimeter must
be connected in parallel in a circuit (see diagram below) in order to measure
voltage. So this means the two test probes should be connected in parallel with
the voltage source, load or any other two points across which voltage needs to
be measured.
6.Touch
the black probe against the first point of the circuitry/wiring.
7.Power
up the equipment.
8.Touch
the other red probe against the second point of test. Ensure you don't bridge
the gap between the point being tested and adjacent wiring, terminals or tracks
on a PCB.
9.Take
the reading on the LCD display.
Finally,
You
can Measure
Solenoid's Voltages.





Copy right © 2017 HUATUI GROUP







